Let’s start with the complete information about the human reproductive system chapter. Read this article “Human Reproductive System” and answer all important questions related to this topic.
Explain the Human Reproductive System
Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same species by existing organisms of a species that is parents. Reproduction is important for the continuation of species.
It may be asexual or sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction takes place in small organisms like a hydra, amoeba, paramecium, etc. Hydra is produced by budding. Animal-like amoeba, paramecium reproduces by binary fission.

Types of Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is the process of producing a new organism from a single parent without the involvement of sex cells or gametes.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the process of producing a new organism from two parents by making use of their sex cells or gametes.
In other words, sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which two sexes, namely, male and female are involved. The male sexual unit is known as male gametes or sperm while the female sexual unit is termed as female gametes or ova.
What is the human reproductive system?
Males and females have different reproductive systems. The reproductive organs of human beings which are Testis in males and ovaries in females become functional only after attaining sexual maturity.
In males, sexual maturity is attained at the age of 13-14 years, but in females at the age of 10-12 years. This age is known as the age of puberty.
Puberty: It is the age at which the sex hormones (or gametes) begin to be produced and the boy or girl becomes sexually mature.
The testes and ovary produce gametes and also secrete hormones like testosterone (the male hormone from the testes) and estrogen and progesterone (female hormones from the ovary).
Male Reproductive system
It consists of portions that produce the germ cells and other portions that deliver the germ cells to the site of fertilization. The main organs of the male reproductive system are the following:
Testes
Testes are the main reproductive organs of the male body that produce sperm. They hang outside the body in scrotal sacs as they need a temperature lower than the body temperature.
Testes also act as endocrine glands and produce male reproductive hormones (testosterone).
Vas deferens
The sperm is carried by a long tube known as the vas deferens of the sperm duct into organs called seminal vesicles, where the sperm gets nourished and stored.
Urethra
It is the tube that carries urine or semen. The urethra carries sperm to an organ called the penis which opens to the outside through a male genital pore.
Penis
It provides a common passage for urine and semen.
Prostate glands
It also produces fluid which is released in the urethra along with the secretion of seminal vesicles. The secretion of accessory glands together with sperms is known as semen.
Sperms
It is a tiny body that consists of mainly genetic materials and a long tail that helps it to move toward the female germ cell.
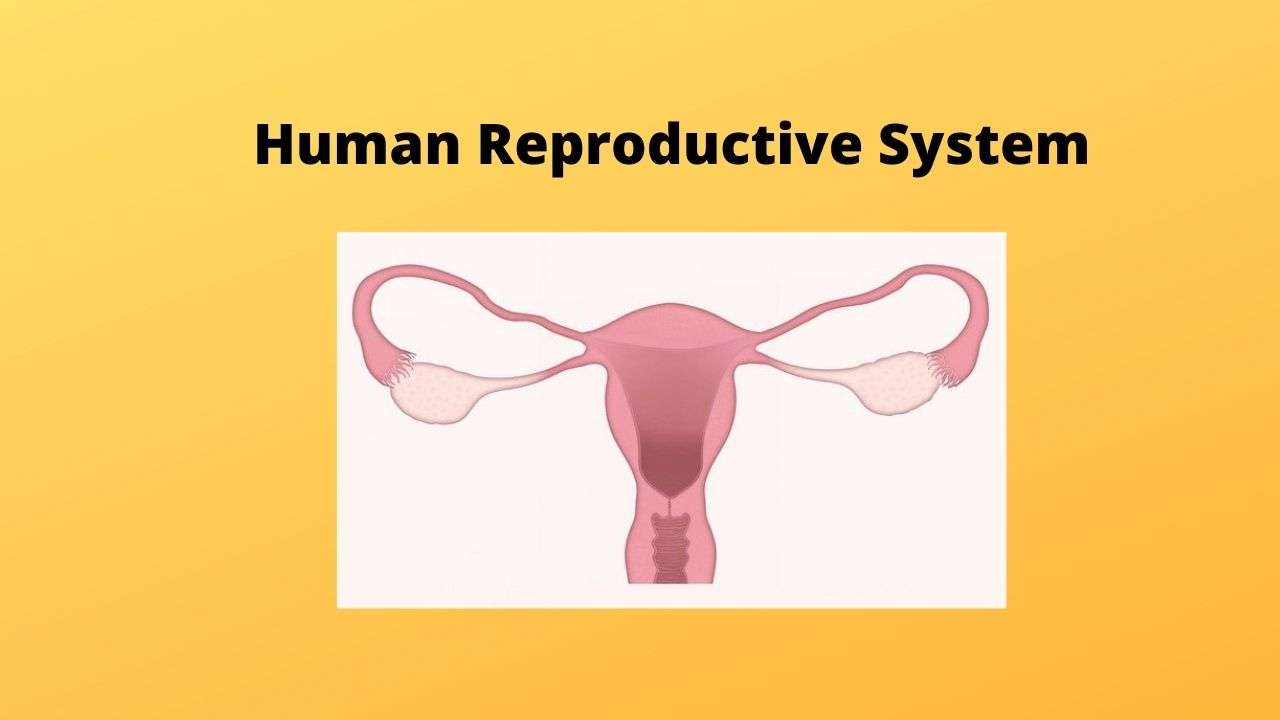
Female reproductive system
The female germ cells or eggs are made in the ovaries and are responsible for the production of some hormones. The main organs of the female reproductive system are:

Ovaries
Ovaries are the main reproductive organs of the female body. They produce ova. Females are born with hundreds of undeveloped female egg cells (ova). These eggs are stored in the ovaries and released every month, after puberty.
Unused eggs dissolve and pass out during the time of menstruation. Ovaries also act as endocrine glands and produce hormones like estrogens and progesterone.
Fallopian tube
It is a pair of long convoluted tubes that carry oval or eggs from the ovary to the uterus. Through the fallopian tube, the egg cell travels to the uterus.
Each ovary is joined to the uterus by a fallopian tube. In the fallopian tube, these are very tiny hairs called cilia that help in the smooth passage of the matured egg to the uterus.
Uterus
The uterus is a bag-like structure that appears like an inverted pear. Its upper portion is broader whereas its lower portion is the narrower called the cervix. It is held in place by ligaments and muscles.
It is the inner lining or the endometrium that is built and shed periodically (28 days) till pregnancy occurs. In that case, it holds the fertilized egg till it develops fully into a baby.
Cervix
The cervix is a ring of muscles located at the lower portion of the uterus. It forms a barrier between the uterus and the vagina.
Vagina
The vagina is an elastic and muscular canal that connects the cervix to the outside of the woman’s body. The vagina is the tube that receives the male organ during sexual intercourse.
Sexual Reproduction in Human beings
The male gametes called sperm are introduced inside the female genital tract (vagina) by the process of copulation or mating. Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube.
Sperms are highly active and move up through the cervix into the uterus and then pass into the fallopian tubes. In the fallopian tube, only one sperm fertilizes the ovum to form a zygote. This is known as fertilization.
Fertilization occurs only when copulation takes place during the ovulatory period. The embryonic development of the zygote begins immediately in the fallopian tube and pregnancy starts while menstruation stops.
The embryo moves down to reach the uterus. The embedding of the embryo in the thick inner lining of the uterus is known as implantation.
Now, a special tissue develops between the uterine wall and the embryo (foetus) called the placenta where the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products takes place.
The period from the development of foetus inside the uterus till birth is known as gestation.
The act of giving birth to a fully developed foetus at the end of the gestation period is known as parturition. The development of the child inside the mother’s body takes approx 9 months.
Adolescence and Puberty
Animals have to reach up to a certain age for reproduction. In human beings, the changes appear in the body after the age of around 11 years. This age is called adolescence or teenage (onset of puberty).
The changes that come are growth in height, body shape, a voice in boys get significantly deeper, increase in mental, intellectual, and emotional maturity, increased activity of sex glands, maturity of ovaries and testes, development of breasts in girls, beard, and mustaches in boys.
All these changes are controlled by hormones. Hormones are the chemicals produced by the endocrine glands that are sent to the target site by the blood.
With puberty, girls start to menstruate every 28-30 days. This is the period when the egg cell matures, the uterine wall becomes thickened.
If fertilization takes place, the zygote is formed and starts developing into an embryo which gets implanted in the uterine wall. This is known as pregnancy.
Frequently Asked Questions of the Human Digestive System
- What is sexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction needs two types of gametes, male gametes (sperm) produced in the male reproductive organs and female gametes (ova) produced in the female reproductive organs.
Generally in animals, sperm from the male and ovum from the female fuse to form a zygote, which grows into a new organism.
- What is menstruation?
Answer: The breakdown and removal of the inner, thick, and soft lining of the uterus along with its blood vessels in the form of vaginal bleeding are known as menstruation. Menstruation is also known as menstrual flow.
- What is a menstrual cycle?
Answer: The cycle of events taking place in the ovaries and uterus every 28 days or roughly 1 month and marked by the menstrual flow is called the menstrual cycle in the human female. The menstrual cycle is also known as the sexual cycle.
- What is sex determination?
Answer: Human cells have 23 chromosomes in each cell. Out of these chromosomes, one pair is the sex chromosome. In males, the sex chromosomes are of two types known as X and Y. In females, both sex chromosomes are similar X and X.
All egg cells contain (22+X) that is 23 chromosomes. A sperm may be either (22+X) or (22+Y). When the 22+X egg is fertilized by 22+X sperm, the zygote 44+XX will develop into a girl, and if the 22+X egg is fertilized by 22+Y sperm, the zygote 44+XY will develop into a boy.
- What are oviparous and viviparous?
Answer: Animals that have internal fertilization like birds but they reproduce by laying eggs are known as oviparous whereas animals that give birth to young ones are known as viviparous.
- Definition of foetus.
Answer: An embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a fetus.
- What is the sex ratio?
Answer: The sex ratio is the ratio of the number of females to the number of males in a population. The female-male sex ratio must be maintained for a healthy society. The female-child sex ratio is declining at an alarming rate in some sections of our society because of reckless female feticide.
Some Important Biology Link
We hope you like this article ” human reproductive system”. Comment below for other important topics.